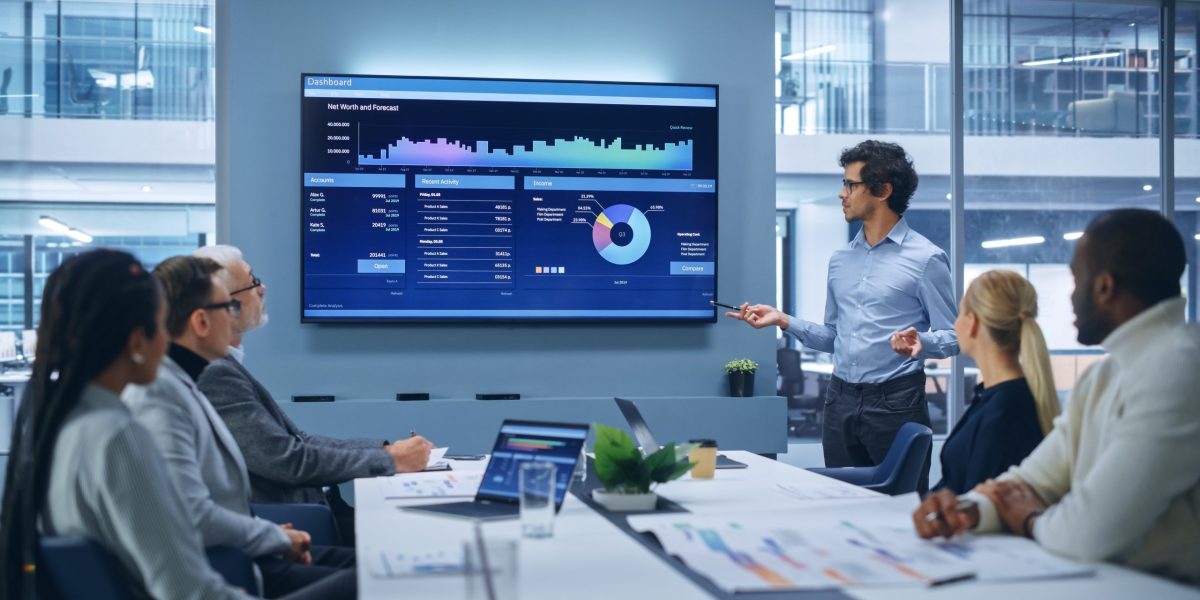
Investing is an essential part of wealth building, but with it comes the inherent risk of loss. One of the most effective strategies to manage this risk is diversification. Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce exposure to any single risk. This approach can help investors achieve more stable returns over time, making it a cornerstone of prudent investment management.
Understanding Diversification
At its core, diversification aims to mitigate risk. When an investor puts all their money into a single asset or a small group of assets, they are highly vulnerable to the performance of those particular investments. If that asset or sector performs poorly, the investor could face significant losses. Diversification, on the other hand, spreads risk by investing in a variety of assets that are likely to respond differently to the same economic event.
For example, during an economic downturn, stocks in the technology sector might suffer, while bonds or stocks in consumer staples (like food and household products) might remain stable or even appreciate. By holding both types of assets, an investor can balance the losses in one area with gains in another, thus reducing the overall volatility of their portfolio.
Types of Diversification
Diversification can be implemented in several ways:
- Asset Class Diversification: This involves spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. Each asset class reacts differently to economic conditions. For instance, while stocks might offer higher returns, they come with higher risk compared to bonds, which are typically more stable.
- Industry Diversification: Investing in various industries can protect against sector-specific risks. For instance, an investor might allocate funds across technology, healthcare, finance, and energy sectors. If the technology sector experiences a downturn, other sectors in the portfolio may perform well, cushioning the overall impact.
- Geographic Diversification: This strategy involves investing in different countries or regions. Economic cycles can vary significantly across the globe. For example, while one country’s economy might be in a recession, another might be experiencing growth. By diversifying geographically, investors can protect their portfolios from localized economic downturns.
The Benefits of Diversification
The primary benefit of diversification is the reduction of risk. While no strategy can eliminate risk entirely, diversification can help investors achieve a more stable and predictable return on their investments. This stability is particularly important for long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning.
Moreover, diversification can enhance returns. By including a mix of assets that respond differently to market conditions, investors can capture gains in various sectors, potentially leading to better overall performance than if they were concentrated in a single asset class or industry.
Another advantage is that diversification allows investors to participate in different market opportunities. For instance, emerging markets might offer higher growth potential than established markets, but with higher risk. A diversified portfolio can include both, allowing investors to benefit from growth while managing the associated risks.
The Challenges of Diversification
While diversification is a powerful tool, it is not without its challenges. Over-diversification can dilute returns, as the benefits of strong-performing assets might be offset by the weaker performance of others. Additionally, diversification requires ongoing management, as market conditions and investment opportunities constantly evolve.
Investors must also be mindful of costs, as managing a diversified portfolio can incur higher fees, particularly when investing in international markets or alternative assets. Therefore, it’s crucial to strike a balance—diversifying enough to reduce risk but not so much that it hampers potential returns or becomes overly complex to manage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diversification is a key strategy for managing risk in an investment portfolio. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions, investors can protect themselves against market volatility and improve their chances of achieving stable, long-term returns. However, it’s important to manage diversification carefully to avoid unnecessary complexity and costs. With the right approach, diversification can be a powerful tool in achieving financial goals and building lasting wealth.